Here Is A Quick Way To Solve A Info About Is Wi Fi Full-duplex

Worldfirst Full Duplex For Wireless Transmission Nokia
Understanding Wi-Fi Communication
Let's talk about Wi-Fi, that magical invisible force that lets you binge-watch cat videos from the comfort of your couch. You've probably never stopped to think about how it all works, have you? Well, prepare to have your mind mildly blown (or at least pleasantly intrigued) as we delve into the world of Wi-Fi communication and tackle the question: Is Wi-Fi full-duplex?
First, a quick vocabulary lesson. "Duplex" refers to the ability to transmit and receive information simultaneously. Think of it like talking on the phone. You can hear someone while you're talking to them. Now, "full-duplex" specifically means you can send and receive data at the same time using the same channel. Is Wi-Fi capable of this simultaneous chatter? That's what we're here to figure out.
Imagine a crowded coffee shop. Everyone's trying to talk at once, and it can get a little chaotic, right? That's kind of what it's like for Wi-Fi devices battling for airtime. They need a way to take turns so messages don't collide into garbled noise. Different technologies govern how they avoid this digital cacophony. So, is Wi-Fi full-duplex? Let's dig deeper.
Think of it as digital choreography. Each device carefully dances to the rhythm of the network, taking its turn to send and receive data. Now, let's explore the technical aspects that influence Wi-Fi's duplex capabilities.
1. The Technical Reality
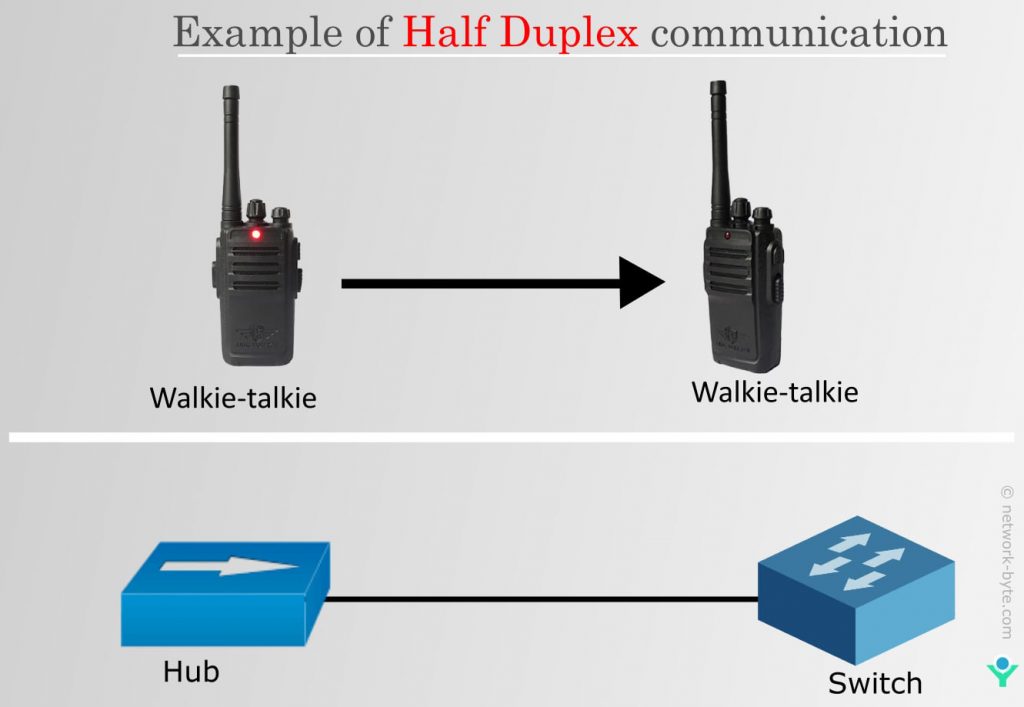
Okay, here's the slightly less exciting (but still important) truth: standard Wi-Fi, as most of us know it, is not full-duplex. It typically operates in what's called "half-duplex" mode. This means devices can either transmit or receive data, but not both at the same time. It's like using a walkie-talkie; you have to say "over" to signal that you're done talking and the other person can start.
So, how does Wi-Fi manage to function if everyone has to wait their turn? The answer lies in technologies like Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance (CSMA/CA). Its a mouthful, I know, but basically, it means a device listens to the wireless channel before transmitting. If it senses activity, it waits a random amount of time and tries again. This helps minimize collisions and allows multiple devices to share the Wi-Fi network.
The "random amount of time" part is crucial. It's like everyone politely hesitating before speaking at a dinner party. Someone eventually jumps in, but the slight pause reduces the chances of everyone talking over each other. Wi-Fi is basically the polite dinner party of the digital world (except with slightly less small talk about the weather).
While this system works relatively well, it does introduce some limitations. Because devices have to take turns, the overall throughput of the network is reduced. The more devices connected, the more competition for airtime, and the slower things can get. This is why your internet seems to crawl when your entire family is streaming Netflix simultaneously.
2. Full-Duplex Wi-Fi
Now, before you resign yourself to a lifetime of half-duplex Wi-Fi, there's some good news! Researchers and engineers are working on technologies that could bring true full-duplex capabilities to Wi-Fi. These advancements aim to overcome the limitations of traditional Wi-Fi and allow for simultaneous transmission and reception.
One promising approach involves advanced signal processing techniques. Think of it like learning to filter out background noise when you're talking to someone in a loud room. These technologies attempt to cancel out the device's own transmitted signal, allowing it to hear incoming signals at the same time. It's a bit like having digital noise-canceling headphones for Wi-Fi.
Imagine the possibilities! Faster downloads, smoother video calls, and less lag in online games. A world where your Wi-Fi doesn't buckle under the strain of multiple devices demanding its attention. Full-duplex Wi-Fi could revolutionize the way we use wireless networks.
However, it's important to note that full-duplex Wi-Fi is still largely in the research and development phase. There are significant technical challenges to overcome, and it may be some time before we see widespread adoption of these technologies in our homes and offices. Still, the potential is there, and the future of Wi-Fi looks brighter than ever.
3. Why Does Duplex Matter Anyway?
You might be thinking, "Okay, so Wi-Fi is usually half-duplex. Big deal! My internet still works (most of the time)." And you'd be right, to an extent. But understanding duplex communication is crucial for optimizing your network and appreciating the ongoing advancements in Wi-Fi technology.
Think about the demands we place on our Wi-Fi networks today. We're constantly streaming videos, downloading files, participating in video conferences, and playing online games. All of these activities require a fast and reliable connection. The limitations of half-duplex Wi-Fi can become increasingly apparent as our usage increases.
By understanding that Wi-Fi devices have to take turns, you can make informed decisions about your network setup. For example, you might consider using wired connections for devices that require the most bandwidth, such as gaming consoles or streaming devices. This frees up the Wi-Fi network for other devices and reduces overall congestion.
Furthermore, understanding the potential of full-duplex Wi-Fi allows you to appreciate the innovations that are being developed to improve our wireless experience. It's like knowing the difference between a horse-drawn carriage and a high-speed train. Both can get you from point A to point B, but one is clearly more efficient and technologically advanced.
4. Looking Ahead
The quest for faster, more efficient wireless communication is far from over. As we move towards a future dominated by the Internet of Things (IoT) and increasingly data-intensive applications, the need for advanced Wi-Fi technologies will only grow stronger. The development of full-duplex Wi-Fi is just one piece of the puzzle.
Researchers are also exploring other innovative approaches, such as millimeter wave (mmWave) technology and multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems. These technologies aim to increase bandwidth, improve signal quality, and reduce interference, all of which contribute to a better overall wireless experience.
Imagine a world where your smart fridge can seamlessly communicate with your grocery store, your self-driving car can navigate traffic with perfect precision, and your virtual reality headset can transport you to another dimension without any lag or buffering. These are just a few of the possibilities that advanced wireless technologies could unlock.
While the road ahead may be challenging, the potential rewards are enormous. By continuing to push the boundaries of wireless communication, we can create a more connected, efficient, and enjoyable world for everyone. And who knows, maybe one day we'll all be using full-duplex Wi-Fi to stream cat videos in glorious, uninterrupted high definition.

FAQ
5. Is it possible to upgrade my current router to support full-duplex Wi-Fi?
Unfortunately, no. Full-duplex Wi-Fi requires new hardware and software implementations that are not compatible with older routers. You'll need to wait for new routers specifically designed with full-duplex capabilities to become available.
6. Does using a wired Ethernet connection bypass the half-duplex limitation of Wi-Fi?
Yes, absolutely! Wired Ethernet connections typically operate in full-duplex mode, meaning devices can send and receive data simultaneously without the limitations of Wi-Fi's half-duplex system. So, if you need the most reliable and fastest connection, a wired connection is always the way to go.
7. How can I improve my Wi-Fi performance with current half-duplex technology?
There are several things you can do! Try positioning your router in a central, open location. Reduce interference by keeping it away from other electronic devices and metal objects. Consider upgrading to a newer Wi-Fi standard (like Wi-Fi 6) for improved efficiency. And limit the number of devices actively using the network at the same time.

Full Duplex Data Communication

