Marvelous Info About What Are The Wires For 3 Phase

How To Wire 3phase
Unveiling the Mystery
Ever wondered how those massive machines in factories or even your friendly neighborhood data center get their oomph? Chances are, it's thanks to the wonder that is 3-phase power. Now, while the name might sound like something straight out of a sci-fi flick, it's actually a clever way to deliver electricity more efficiently than your standard single-phase household current. But what's the secret ingredient? Yep, you guessed it: wires! Let's untangle this electrical enigma together.
1. So, What Exactly Are We Talking About?
Think of 3-phase power as having three separate sources of electricity, all working together in harmony. Each source, or "phase," delivers its power slightly offset from the others. This staggered delivery creates a smoother, more consistent flow of energy, perfect for those heavy-duty applications we mentioned earlier. Its like having three people pushing a swing instead of just one; much more power and less jerky, right?
This efficiency boils down to the way electrical motors work. A three-phase motor produces a rotating magnetic field, which is what makes it spin. This rotating field is created by the interaction of the currents in the three phases. Because the phases are offset, the magnetic field is much smoother and more consistent than in a single-phase motor, leading to greater efficiency and less vibration. Imagine trying to spin a top by flicking it once every three seconds versus flicking it rapidly and continuously the latter is much more efficient!
Now, lets get down to brass tacks. At its simplest, a 3-phase system requires at least three wires. These are your "hot" wires, each carrying one of the three phases of electricity. But hold on, there's usually more to the story! In many 3-phase systems, a fourth wire, called the neutral wire, is also present. The neutral provides a return path for the current, ensuring a balanced system and preventing voltage imbalances. It's like a safety valve, ensuring everything plays nicely together. So, three wires minimum, four wires often got it?
Understanding the wiring configuration is key for proper installation and maintenance. Incorrect wiring can lead to serious problems, including equipment damage, electrical fires, and even personal injury. Always consult a qualified electrician when working with 3-phase power! Its not something to DIY unless you really, really know what youre doing. Think of it like performing surgery on yourself — probably not a good idea.

Delving Deeper
Okay, weve established that 3-phase systems need at least three wires. But the way those wires are connected can vary, leading to different configurations. The two most common configurations you'll encounter are "Delta" and "Wye" (also sometimes referred to as "Star"). Each has its own advantages and disadvantages, making it suitable for different applications.
2. The Delta Connection
Imagine a triangle. In a Delta configuration, the three phases are connected in a closed loop, forming a triangle (hence the name!). There's no neutral wire in a standard Delta setup. This configuration is often used in industrial settings where high power is required. The voltage between any two wires in a Delta system is the same, making it a robust and reliable choice for powering heavy machinery.
One key benefit of the Delta configuration is its resilience. If one phase fails, the other two phases can still deliver power, although at a reduced capacity. This "limp along" capability can be crucial in maintaining operations in critical applications. However, the lack of a neutral wire can also be a disadvantage in some cases. It means that Delta systems are less suitable for powering single-phase loads, like lights and small appliances. Delta connections generally handle motor loads effectively but are less versatile for mixed loads.
Delta systems can also have a "high leg" or "wild leg" configuration. This involves grounding one of the phase conductors, resulting in one phase having a higher voltage to ground than the other two. This configuration is sometimes used to provide a limited amount of single-phase power, but it requires careful planning and marking to avoid accidental overvoltage. Working with a "high leg" Delta system can be tricky. Ensure qualified personnel understand the system and are prepared with the appropriate safety measures!
Think of the Delta configuration as the workhorse of the 3-phase world. It's strong, reliable, and designed for heavy lifting. While it may not be the most versatile option, it excels at what it does: delivering raw power to industrial machinery.
3. The Wye Connection
Now, picture a star, or the letter "Y." In a Wye configuration, the three phases are connected to a common point, called the neutral point. This neutral point is typically grounded, providing a stable reference for the system. The Wye configuration is often used in both industrial and residential settings, offering a balance of power and versatility.
The presence of a neutral wire in the Wye configuration is a significant advantage. It allows for both 3-phase and single-phase loads to be powered from the same system. You can connect 3-phase motors to the three "hot" wires, and then tap off single-phase power between each hot wire and the neutral for lighting, outlets, and other smaller appliances. This makes the Wye configuration a much more versatile option than the Delta configuration.
Another advantage of the Wye configuration is that it can provide a lower voltage to ground than the Delta configuration. This can improve safety and reduce the risk of electrical shock. The lower voltage is achieved because the voltage between each phase and the neutral point is lower than the voltage between any two phases. This makes the Wye connection a popular choice for applications where safety is a top priority.
The Wye configuration is like the Swiss Army knife of 3-phase power. It's versatile, adaptable, and can handle a wide range of tasks. Whether you're powering heavy machinery or keeping the lights on in your home, the Wye configuration is a reliable and efficient choice.

3 Phase Distribution Board Layout And Wiring Diagram / Three DB
Wire Colors
Okay, so we know we need at least three wires for 3-phase power, and sometimes a neutral. But how do you tell them apart? That's where wire colors come in! Color coding helps electricians and technicians quickly identify the different phases and the neutral wire, ensuring proper connections and preventing potentially dangerous mistakes. Think of it as a visual language that speaks volumes about the electrical system.
4. North American Standards
In North America, the standard color codes for 3-phase wiring are as follows: Phase A is typically black, Phase B is red, and Phase C is blue. The neutral wire is white or gray, and the ground wire is green or bare copper. These colors are widely adopted throughout the United States, Canada, and Mexico, making it easier for electricians to work on 3-phase systems across the continent.
However, it's important to note that these color codes are not universal. Different countries and regions may have their own standards. For example, in Europe, the color codes are different (more on that later). Therefore, it's always crucial to verify the specific color codes used in a particular installation before working on it. Never assume that the colors are the same as what you're used to!
The ground wire, typically green or bare copper, plays a vital role in safety. It provides a path for fault current to flow back to the source, tripping the circuit breaker or blowing the fuse and preventing electrical shock. It's essential to ensure that the ground wire is properly connected and that it is sized correctly to handle the expected fault current. A properly functioning ground wire is a critical component of any electrical system.
Think of wire colors as the traffic signals of the electrical world. They provide clear and unambiguous information about the purpose of each wire, helping to prevent accidents and ensure safe and efficient operation. Always pay attention to the colors and double-check your connections before energizing any 3-phase system.
5. European Standards
Across the pond in Europe, the color codes for 3-phase wiring are a bit different. Phase L1 is typically brown, Phase L2 is black, and Phase L3 is gray. The neutral wire is blue, and the ground wire is green-yellow (a combination of both colors). These colors are widely used throughout Europe and are standardized by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
The differences in color codes between North America and Europe can sometimes lead to confusion, especially for electricians who work internationally. It's essential to be aware of these differences and to always verify the specific color codes used in a particular installation. Using the wrong color code can have serious consequences, leading to incorrect connections and potentially dangerous situations.
Even within Europe, there can be some variations in color codes, especially in older installations. It's always a good idea to consult the local regulations and standards to ensure that you are using the correct colors. Remember, safety is paramount, and taking the time to verify the color codes can save you a lot of trouble in the long run.
So, whether you're working in North America, Europe, or anywhere else in the world, always remember to check the color codes before working on any 3-phase system. A little bit of knowledge can go a long way in preventing accidents and ensuring a safe and successful installation.
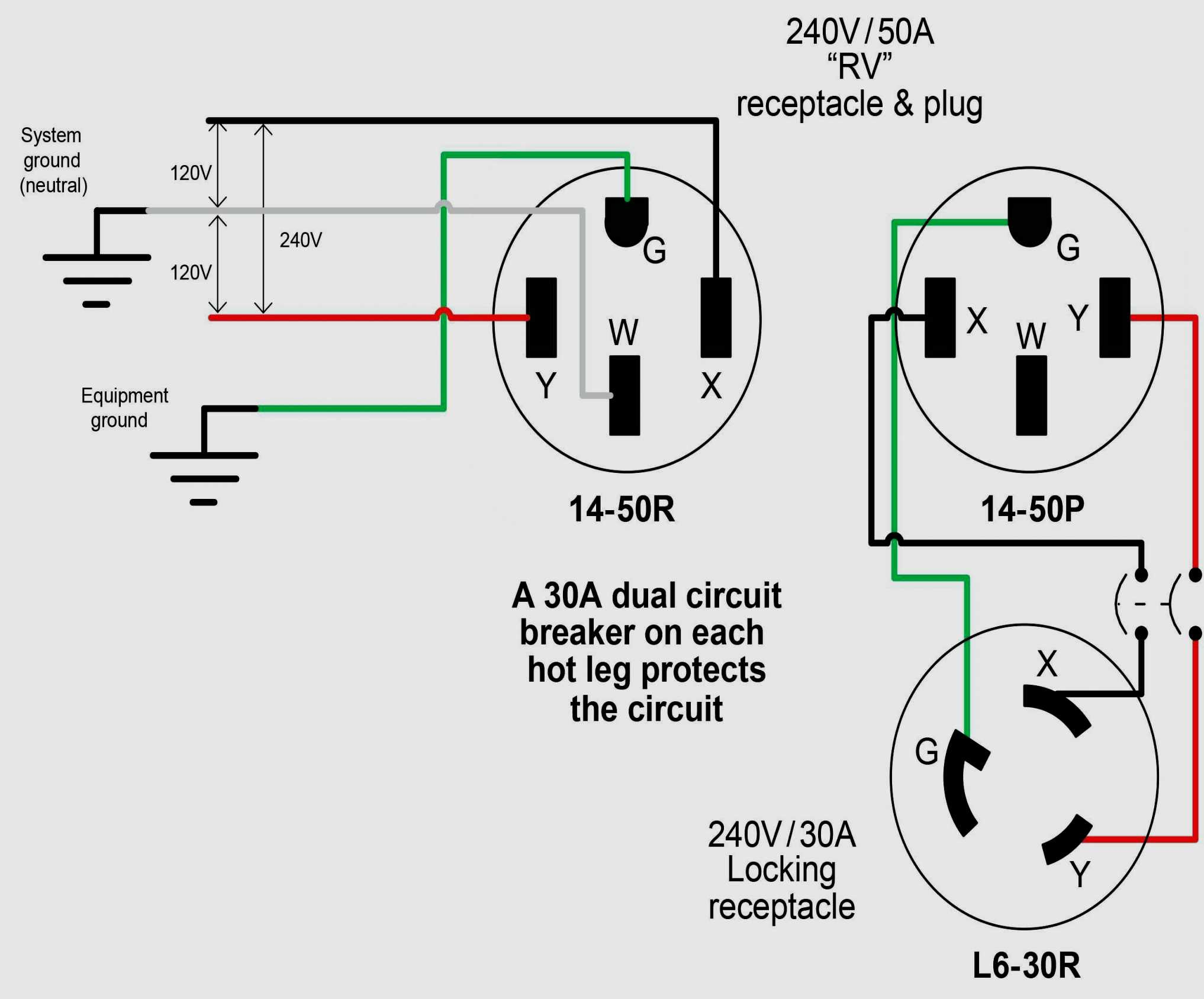
How To Wire Three Phase Plug
Practical Applications
Now that we know what the wires are for and how they're colored, let's talk about where you're likely to encounter 3-phase power in the real world. It's not just confined to massive factories and data centers; you might be surprised at some of the other places it pops up!
6. Industrial Settings
As we've mentioned before, 3-phase power is the go-to choice for industrial applications. Heavy machinery like motors, pumps, and compressors all benefit from the smooth and efficient power delivery that 3-phase provides. Think about factories, manufacturing plants, and even water treatment facilities — they all rely heavily on 3-phase systems to keep things running.
The higher power capacity of 3-phase systems allows them to handle the demanding loads of industrial equipment. Single-phase power simply wouldn't be able to keep up with the energy demands of these applications. 3-phase power provides a more consistent voltage and current, reducing stress on equipment and extending its lifespan. It's like giving your machinery a constant supply of premium fuel, ensuring it runs smoothly and efficiently for years to come.
Another advantage of 3-phase power in industrial settings is its ability to handle unbalanced loads. In many industrial facilities, the electrical loads are not evenly distributed across the three phases. 3-phase systems are designed to handle these imbalances, providing stable and reliable power even when the loads are not perfectly balanced. This is crucial for maintaining consistent operation and preventing equipment failures.
So, if you ever find yourself in an industrial setting surrounded by humming machinery and blinking lights, chances are you're in the presence of 3-phase power. It's the unsung hero that keeps the wheels of industry turning.
7. Commercial Buildings
While you might not see it directly, 3-phase power is also commonly used in commercial buildings like office complexes, shopping malls, and hospitals. These buildings often have significant electrical demands, powering everything from lighting and HVAC systems to elevators and computer equipment. 3-phase power provides the capacity and reliability needed to keep these buildings running smoothly.
Large HVAC systems, in particular, often require 3-phase power to operate efficiently. These systems consume a significant amount of energy, and 3-phase power provides a more stable and consistent power supply, reducing energy costs and improving performance. Similarly, elevators and escalators rely on 3-phase motors to lift and transport people, ensuring smooth and reliable operation.
Even smaller businesses can benefit from 3-phase power. Computer servers, which are essential for many modern businesses, often require 3-phase power to operate reliably. These servers are sensitive to voltage fluctuations and power outages, and 3-phase power provides a more stable and consistent power supply, minimizing the risk of data loss and downtime.
So, next time you're in a commercial building, take a moment to appreciate the hidden power that keeps everything running smoothly. 3-phase power is the silent workhorse that powers our businesses and keeps our economy moving.
8. Residential Areas
While 3-phase power is not as common in residential areas as single-phase power, it is becoming increasingly popular, especially in larger homes with high electrical demands. Some homes may have 3-phase power to run high-power appliances like electric vehicle chargers, large air conditioning units, or even home workshops with heavy-duty tools.
Electric vehicle chargers, in particular, are driving the demand for 3-phase power in residential areas. These chargers can draw a significant amount of power, and 3-phase power provides a more efficient and reliable way to deliver that power. As electric vehicles become more popular, the demand for 3-phase power in residential areas is likely to increase.
Another reason why some homes may have 3-phase power is if they are located near industrial or commercial areas. In some cases, it may be more cost-effective to run 3-phase power to the home rather than installing a separate single-phase service. This is especially true if the home is located on a large property and has significant electrical demands.
While 3-phase power may not be the norm in residential areas just yet, it is a growing trend that is likely to continue as our homes become more energy-intensive. So, keep an eye out for it — you might just find it powering your neighbor's electric car!
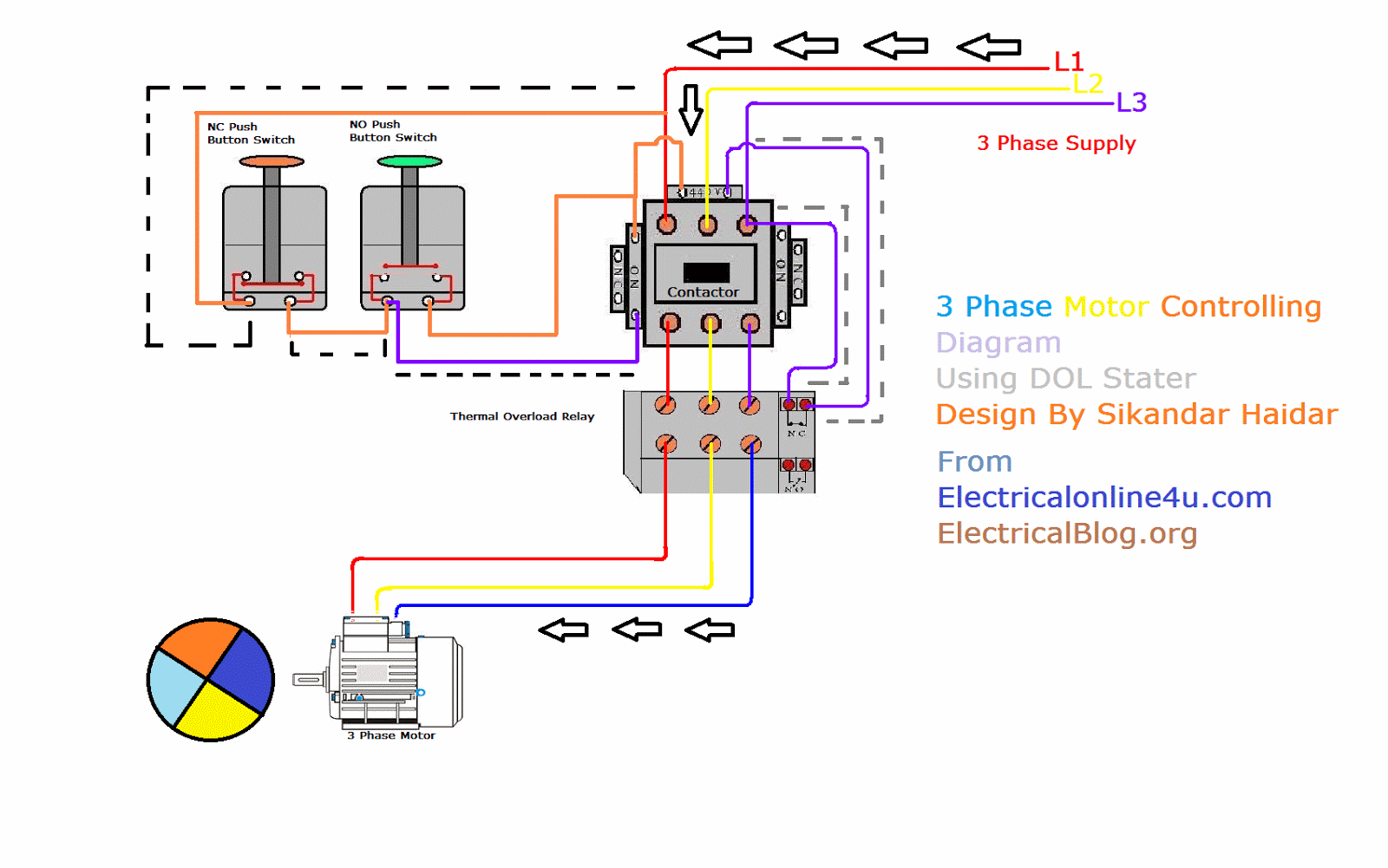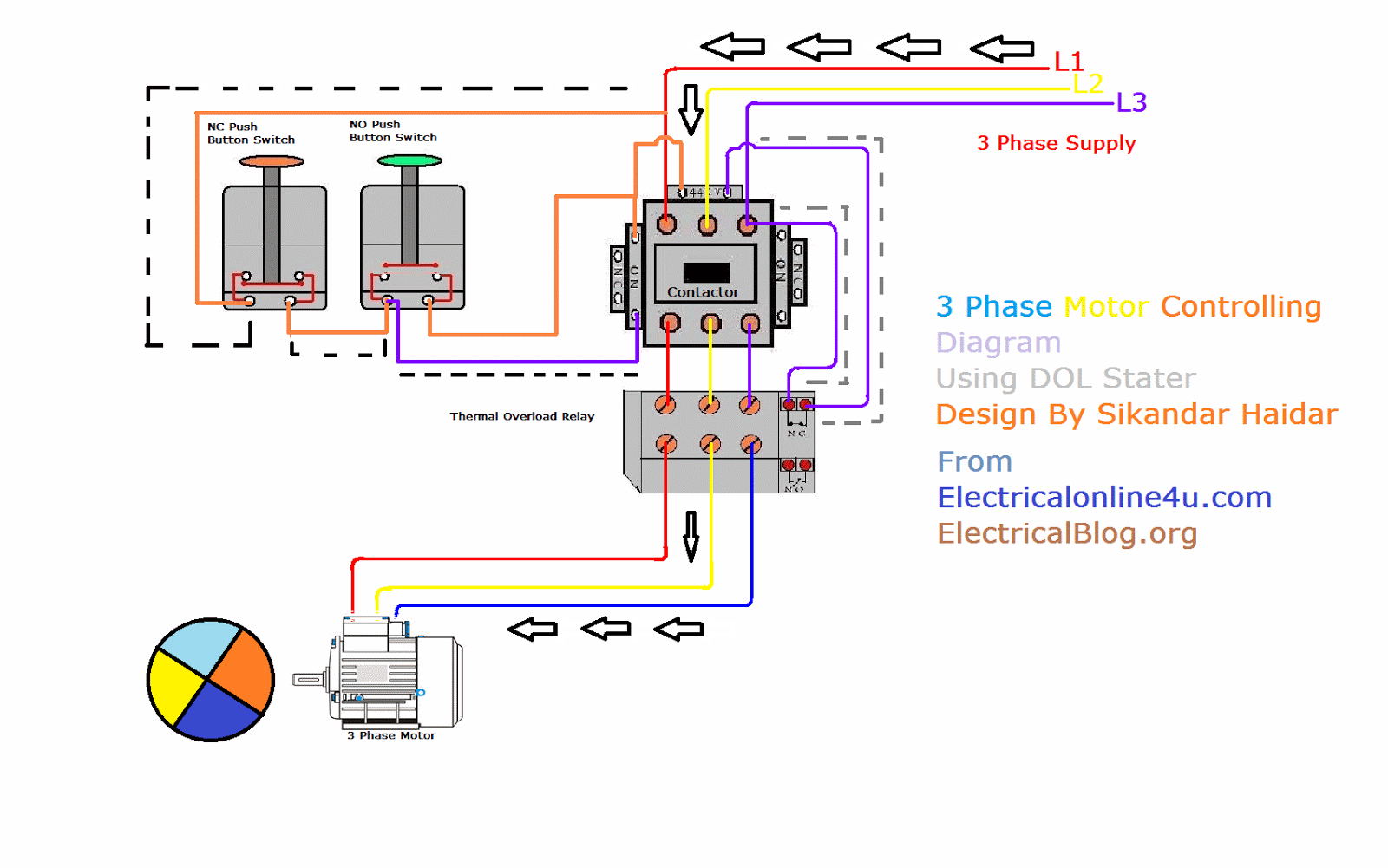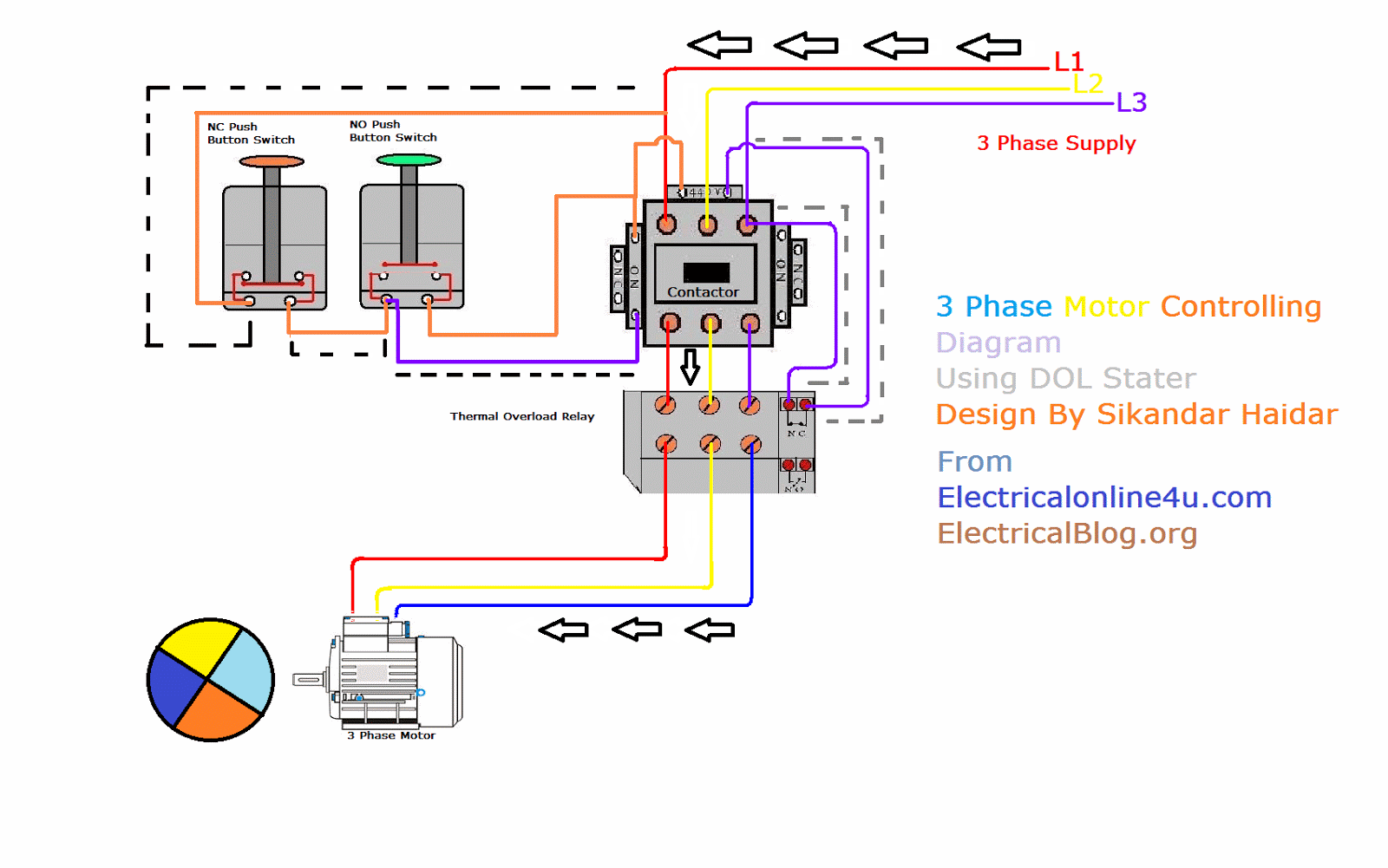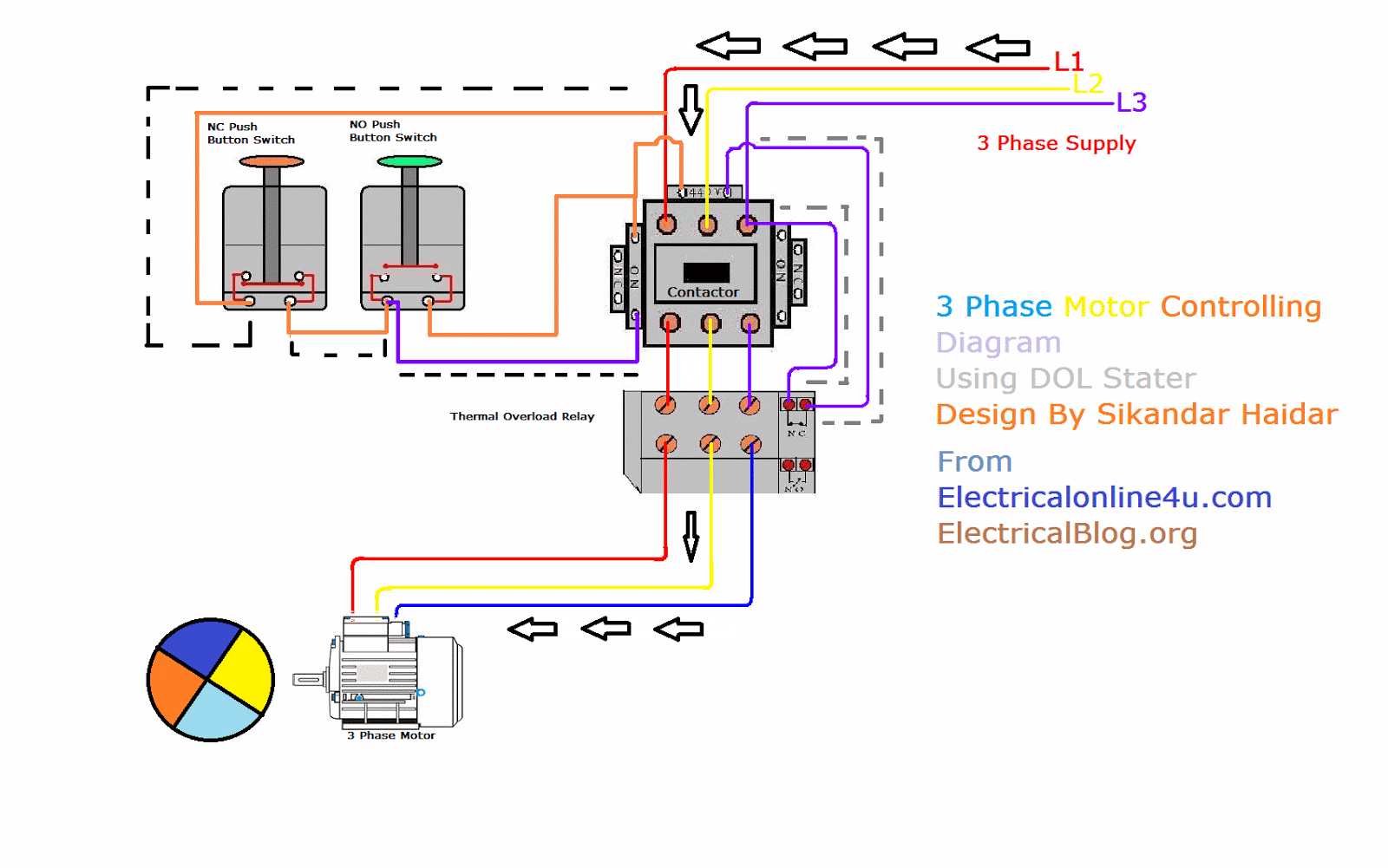
Troubleshooting
Even with the best planning and installation, things can sometimes go wrong with a 3-phase power system. Knowing how to troubleshoot common problems can save you time, money, and potentially prevent serious damage. But remember: always prioritize safety and consult a qualified electrician if you're not comfortable working with electricity.
9. Common Issues
One of the most common issues with 3-phase systems is voltage imbalance. This occurs when the voltage between the three phases is not equal. Voltage imbalance can lead to reduced equipment efficiency, overheating, and even premature failure. It can be caused by unbalanced loads, faulty transformers, or loose connections. Identifying the source of the imbalance is the first step in resolving the problem.
Another common issue is phase loss, which occurs when one of the three phases is lost or interrupted. Phase loss can cause motors to overheat and potentially burn out. It can be caused by blown fuses, tripped circuit breakers, or damaged wiring. Identifying the cause of the phase loss and restoring the missing phase is crucial to prevent equipment damage.
Harmonic distortion is another potential problem in 3-phase systems. Harmonics are unwanted frequencies that can interfere with the normal operation of electrical equipment. They can be caused by non-linear loads, such as electronic ballasts and variable frequency drives. Harmonic distortion can lead to overheating, equipment malfunction, and even system instability. Mitigating harmonic distortion often requires specialized equipment, such as harmonic filters.
Think of troubleshooting a 3-phase system like being a detective. You need to gather clues, analyze the evidence, and use your knowledge to identify the culprit. With careful observation and a systematic approach, you can often track down the source of the problem and get the system back up and running.
10. Safety First
Before attempting any troubleshooting on a 3-phase system, it's crucial to take the necessary safety precautions. Always disconnect the power before working on any electrical equipment. Use a voltage tester to verify that the power is off. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as insulated gloves and safety glasses. And never work alone! Having a second person present can be invaluable in case of an emergency.
If you're not comfortable working with electricity, or if you're unsure about how to troubleshoot a particular problem, it's always best to consult a qualified electrician. They have the knowledge, experience, and tools to safely and effectively diagnose and repair 3-phase systems. Trying to fix a problem yourself without the proper training can be dangerous and could potentially lead to serious injury or property damage.
Remember, safety is always the top priority. Don't take any unnecessary risks. If you're not sure, ask for help. It's better to be safe than sorry.
So, whether you're a seasoned electrician or just a curious homeowner, understanding the basics of 3-phase power and how to troubleshoot common problems can be invaluable. With a little knowledge and a lot of caution, you can keep your 3-phase systems running smoothly and safely.
