What Everybody Ought To Know About Does Tesla Use AC Or DC Charging

EV Charging The Difference Between AC And DC EVBox
Unraveling the Mystery
1. Understanding the Basics
So, you've got a Tesla, or you're thinking about getting one. Awesome choice! But now you're staring at that charging port and wondering, "What kind of juice does this thing slurp? Is it AC or DC?" Well, buckle up, because we're about to demystify the world of Tesla charging. The answer, in short, is both! But, as with most things in life, its not quite that simple.
Think of it like this: your Tesla, like most electric vehicles, has an onboard charger. This little gizmo takes Alternating Current (AC) — the kind of electricity that flows through your home outlets — and converts it into Direct Current (DC), which is what the battery actually needs to store energy. Its kind of like a translator, making sure the battery understands what the outlet is saying.
However, there are also Direct Current Fast Charging (DCFC) stations, sometimes referred to as Level 3 chargers or Superchargers. These stations bypass the onboard charger entirely and deliver DC electricity directly to the battery. Imagine skipping the translator and speaking the battery's native language! This is why DC fast charging is significantly quicker.
Ultimately, the type of charger you use depends on how quickly you need to charge and where you're charging. Home charging usually utilizes AC, while public fast-charging stations predominantly use DC. Lets dig a little deeper, shall we?
EV Charging Stations (All You Need To Know)
AC Charging
2. Home Sweet Home Charging
Alright, lets talk AC charging. This is your bread-and-butter, everyday charging situation. Imagine plugging your Tesla into a regular wall outlet at home. That's AC charging in action! Its convenient, especially if you charge overnight while you're sleeping (and your car is too, essentially).
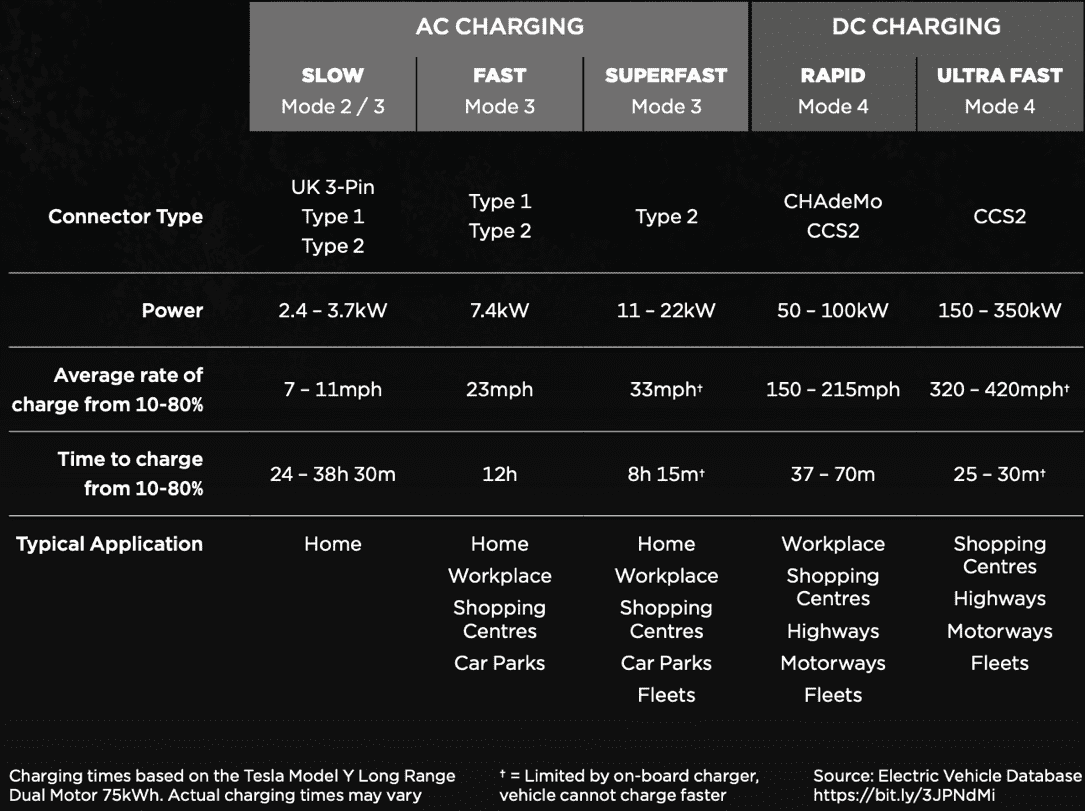
AC charging is typically divided into two levels: Level 1 and Level 2. Level 1 is your standard 120-volt outlet. It's the slowest method, adding only a few miles of range per hour. Level 2, using a 240-volt outlet (like the one your dryer uses), is much faster, adding significantly more miles per hour. Installing a Level 2 charger at home is a game-changer for Tesla owners.
The downside of AC charging is its speed, or lack thereof. If you're in a hurry, AC charging wont be your best bet. Think of it as slowly sipping a cup of coffee versus chugging an energy drink. It gets the job done, but it takes its sweet time.
But the beauty of AC charging lies in its accessibility. AC power is everywhere! Which makes it convenient for topping up your Tesla at home, work, or even some public charging stations. Plus, AC chargers are generally less expensive to install compared to their DC counterparts.

AC Vs DC Charging What’s The Difference? 1C EV
DC Fast Charging
3. Supercharging Power
Now, lets crank things up a notch and dive into the world of DC fast charging, often called Supercharging in the Tesla universe. This is where you get your "fill 'er up" experience, adding a substantial amount of range in a relatively short period.
DC fast chargers deliver DC electricity directly to your Tesla's battery, bypassing the onboard charger. This allows for much higher power levels, resulting in significantly faster charging times. Think of it like a firehose versus a garden hose. Both deliver water, but one does it with a whole lot more oomph!
The primary advantage of DC fast charging is, well, speed. Its perfect for long road trips or when you need a quick boost before heading out. Superchargers are strategically located along major highways, making them ideal for long-distance travel. Teslas Supercharger network is a key selling point for many owners, providing a reliable and widespread charging infrastructure.
The only real drawback of DC fast charging is that its not as widely available as AC charging, and it can be more expensive per kilowatt-hour. Also, frequent DC fast charging can, theoretically, slightly degrade your battery over time, although Tesla's battery management system is designed to mitigate this effect. So, while it's great for quick boosts, its generally recommended to rely on AC charging for everyday use.
The Difference Between AC & DC Charging Ev Installed
The Tesla Onboard Charger
4. Converting AC to DC
Let's give some credit where it's due: the Tesla's onboard charger. This often-overlooked component is the key to AC charging. It takes the AC electricity from your wall outlet and converts it into DC electricity that your battery can actually use and store. Without this handy device, AC charging would be impossible!
The onboard charger has a specific charging rate, measured in kilowatts (kW). This determines how quickly your Tesla can charge when using AC power. Different Tesla models may have different onboard charger capacities. The higher the kW rating, the faster the charging speed, theoretically. However, real-world charging speeds also depend on the amperage of the AC outlet and the car's state of charge.
It's important to understand your Tesla's onboard charger capacity to optimize your AC charging experience. For instance, if your car has an 11kW onboard charger, but you're only plugging into a 3kW outlet, you won't be getting the maximum charging speed. It's like trying to fill a swimming pool with a drinking straw — technically possible, but not exactly efficient!
While the onboard charger is essential for AC charging, it's bypassed entirely during DC fast charging. This is why DC fast charging is so much faster: it's delivering power directly to the battery without having to go through the AC-to-DC conversion process.
Tesla Launches New EV Charging Battle, But The Plug War Is Already Over
Maximizing Your Tesla Charging Experience
5. Tips and Tricks for Efficient Charging
Okay, now that you understand the basics of AC and DC charging, lets talk about how to get the most out of your Tesla's charging capabilities. Here are a few tips and tricks to maximize your charging experience:
Install a Level 2 charger at home: Seriously, this is a game-changer. A Level 2 charger will significantly reduce your charging times, making it much more convenient to keep your Tesla topped up. Consider this an investment in your sanity, trust me.
Utilize off-peak charging: Many utility companies offer lower electricity rates during off-peak hours (usually overnight). Take advantage of these lower rates by scheduling your Tesla to charge during these times. You'll save money and help balance the grid.
Plan your road trips strategically: Use Tesla's trip planner to map out your route and identify Supercharger locations along the way. This will help you ensure that you have enough range to reach your destination without any unexpected surprises. Running out of battery is not a fun experience.
Don't always charge to 100%: Unless you need the full range, it's generally recommended to charge your Tesla to around 80-90% for everyday use. This can help prolong battery life. Think of it like stretching before a workout; it keeps things limber.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
6. Can I use any charging station with my Tesla?
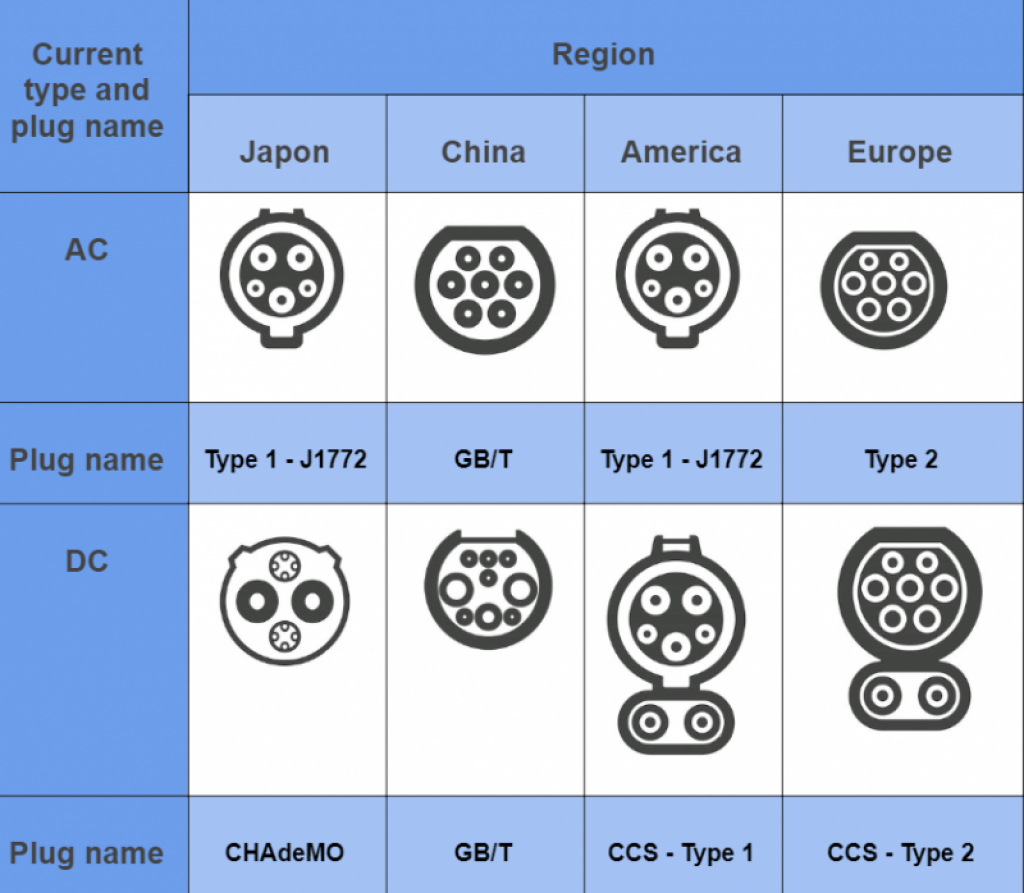
Yes, but with adapters. Tesla uses a proprietary charging port in North America. For AC charging at non-Tesla stations, you'll typically need a J1772 adapter (which usually comes with the car). For DC fast charging, you'll need a CCS adapter for CCS Combo chargers in North America. In Europe, Teslas use the CCS standard, so adapters are less often needed.
7. Is it bad to always Supercharge my Tesla?
While occasional Supercharging is fine, relying solely on DC fast charging can, theoretically, accelerate battery degradation over time. It's best to use AC charging for everyday needs and reserve Supercharging for road trips or when you need a quick boost. Basically, everything in moderation!
8. How long does it take to charge a Tesla?
Charging times vary depending on the charging method, battery size, and initial state of charge. Level 1 charging can take several hours to add a significant amount of range, while Level 2 charging is much faster. Supercharging can add hundreds of miles of range in under an hour.